Back to list
Back to list
Source: Founder Securities
The process of "intelligence", "electricity", "network connection" and "three modernizations" of automobiles continues to accelerate, and the demand for various automotive semiconductors has increased to varying degrees. Vehicle-grade MCUs are a type of vehicle-mounted MCU with a wide range of application scenarios. Chips and automotive-grade MCUs have broad market prospects.
Vehicle-grade MCUs are one of the "protagonists" of this round of "core-lack" incident. Multiple factors have contributed to a serious "core-lack" crisis in the automotive industry chain, which has led to huge difficulties in global automobile production. Advanced MCUs are still one of the most in-demand types of automotive chips. The epidemic will eventually pass, and the development trend is unstoppable. The automotive electronic and electrical (E/E) architecture is changing, and the demand for automotive MCUs will change accordingly.
From the automotive industry chain to the automotive MCU chip
MCU (Microcontroller Unit) is called Microcontroller Unit or SCM, which appropriately reduces the frequency and specifications of the central processing unit, and integrates memory, counters, peripheral interfaces, etc. on a single chip to form a chip-level computer. Widely used in consumer electronics, Internet of Things, automotive electronics, industrial control and other fields.
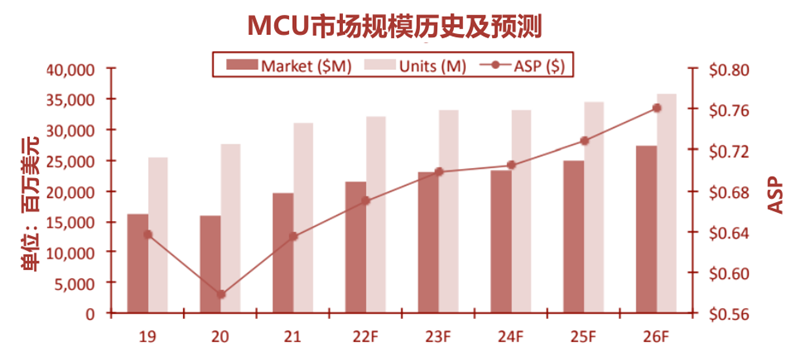
▲MCU market size history and forecast
According to IC Insight data, after the global MCU market fell 2% under the impact of the new crown pneumonia epidemic in 2020, with the strong economic recovery in 2021, MCU sales climbed 23% to a record $19.6 billion.
IC Insights forecasts that global MCU sales will grow 10% in 2022 to an all-time high of $21.5 billion, with automotive MCU growth outpacing most other end markets.
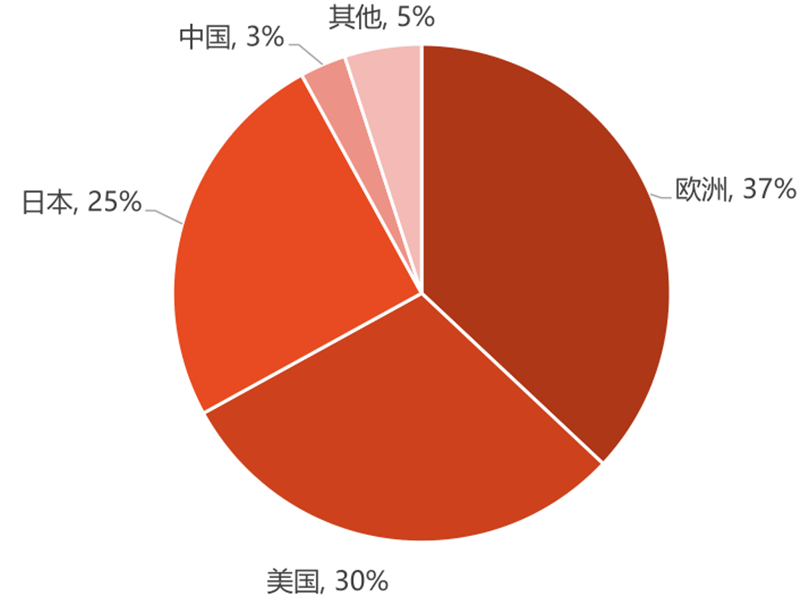
According to IC Insights mid-2021 data, despite the impact of chip shortages and the epidemic, global automotive MCU sales are expected to reach US$7.6 billion in 2021, an increase of 23% compared with 2020, of which more than three-quarters of Automotive MCU sales came from 32-bit and were about $5.8 billion.
Global automotive MCU sales are expected to grow by 14% and 16% in 2022 and 2023, respectively, reaching a scale of $10 billion by 2023.
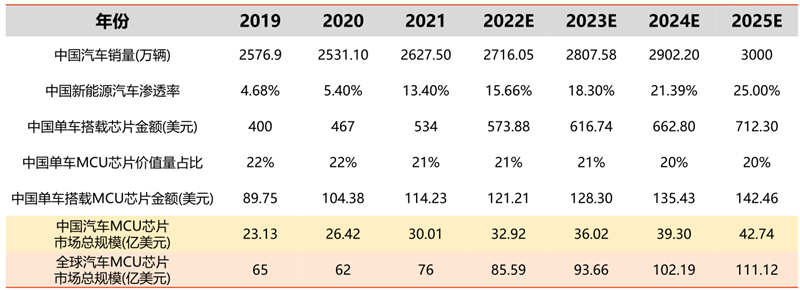
At present, under the impact of the epidemic, the sales of new energy vehicles have increased against the trend. In the face of the huge downstream market demand, OEMs have entered the stage of active inventory addition, and the demand for automotive-grade chips will continue to remain high. It is expected that the high demand for automotive-grade MCU chips will continue until the end of 22. The investment in capacity expansion is expected to achieve a substantial increase in production scale in 23 years.
Typically, it takes 12-16 weeks for an MCU to complete in-house production. Compared to 22Q1, the shortage of MCUs is more pronounced, and most MCUs are in shortage, especially STMicroelectronics and NXP. Car MCUs are currently only available from Renesas and Cypress, with a lead time of 32-45 weeks, and other brands are in short supply.
In 2022, automotive MCU orders are almost full and prices continue to rise. Among them, STMicroelectronics announced on March 24 that it will increase the prices of all product lines in the second quarter. Today, the demand for MCUs is not just quantitative. With the promotion of emerging industries, new requirements for low power consumption, high computing power, customization, and dedicated peripherals are gradually increasing.
In 2021, due to the shortage of chips, the global auto market will reduce the cumulative production of about 10.2 million units. As of May 15, due to chip shortages, the global auto market has cut production by about 1.72 million vehicles this year. Among them, the cumulative production reduction in the Chinese auto market increased to 92,000 units, accounting for 5.3% of the global cumulative production reduction.
In addition to the shortage of chips, the "three modernizations" of automobiles are also an important driving factor for MCUs:
Intelligence: Currently, the penetration rate of L0-L2 autonomous driving is still rapidly increasing, and the demand for intelligent driving will continue to increase the amount of ECU and MCU. As the core of the internal calculation and processing of the automotive electronic system, MCU is the key to realize the intelligentization of the car. According to the iSuppli report, MCU chips account for about 30% of the semiconductor devices used in a car. This means that each car needs to use at least 70 MCU chips.
Electrification: Global electrified EV sales will reach 675,000 units in 2021, up 108% from 2020, and despite the extreme year-on-year growth rate in 2020, sales in 2021 will still be substantial due to the low base in 2020.
Networking: The increase of IoT devices has increased the demand for networking capabilities. As a key component of networking devices, MCUs also need to take into account cost and power consumption, prompting wireless MCU solutions to quickly enter the industry's vision.
The golden development period of semiconductor equipment is coming
With the gradual increase of car functions, especially after the "three modernizations" of automobiles, the traditional distributed architecture increases the functions of the car by adding ECUs, which results in a waste of computing power, complicated lines in the car, low efficiency in the use of car space, difficult system upgrades, and new ECUs. Due to the disadvantages of increasing marginal cost, it is the general trend to use domain controllers to reasonably integrate ECU functions.
ECU (Electronic Control Unit) is an electronic control unit, which is a "computer" that controls the functions of the car. Its interior includes MCU, memory, input/output interface, analog-to-digital converter (A/D) and other integrated circuits. In distributed mode, a single ECU controls a certain function of the car. To increase the function of the car, it is necessary to increase the ECU, and the increase of the ECU will bring the increase of the MCU.
DCU (Domain Control Unit) domain control unit refers to the controller that centrally controls some functions of the car. Its chips are mainly SoC chips, which include high-power microprocessors, memory, and input/output interfaces. Under domain control, some functions of the car are integrated and controlled by the DCU, and the reduction in the number of ECUs leads to a decrease in the usage of MCUs.
There are many functions in the car, some functions have existed since the birth of the car, and some functions have been used and retained in the car at a certain time with the development of the automobile industry. Under the trend of intelligence, various emerging functions are accelerated to add applications and continue to update and iterate. Bosch divides the whole vehicle into power domain, chassis domain, body domain, cockpit domain, and autonomous driving domain according to car functions. Based on Bosch's conception, the power domain, chassis domain and body domain that integrate traditional functions are grouped together, and the cockpit domain and autonomous driving domain are grouped into emerging function groups.

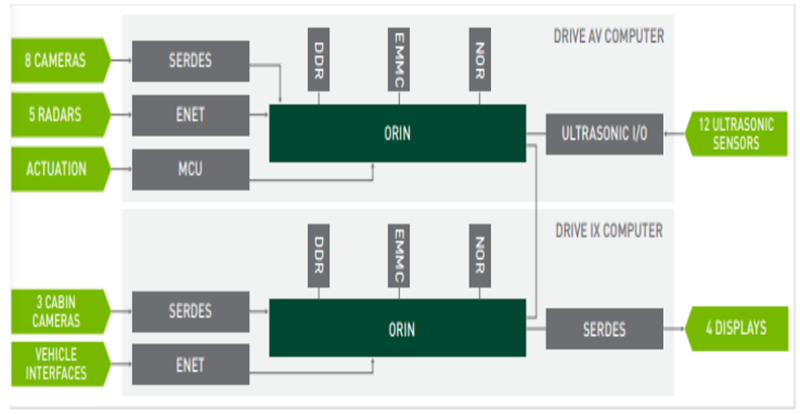
▲ After the ADAS functional domain is concentrated, the SoC takes the leading position
Take the NVIDIA DRIVE Orin™ SoC product as an example: it integrates a new generation of GPU architecture and Arm Cortex-A78AE CPU core, which are high computing power processors, and the SoC chip controls multiple autonomous driving sensors. Controlling many sensors no longer requires multiple MCUs, but is controlled by the domain master chip. The function of the MCU in this scheme is mainly related to the peripheral drive.
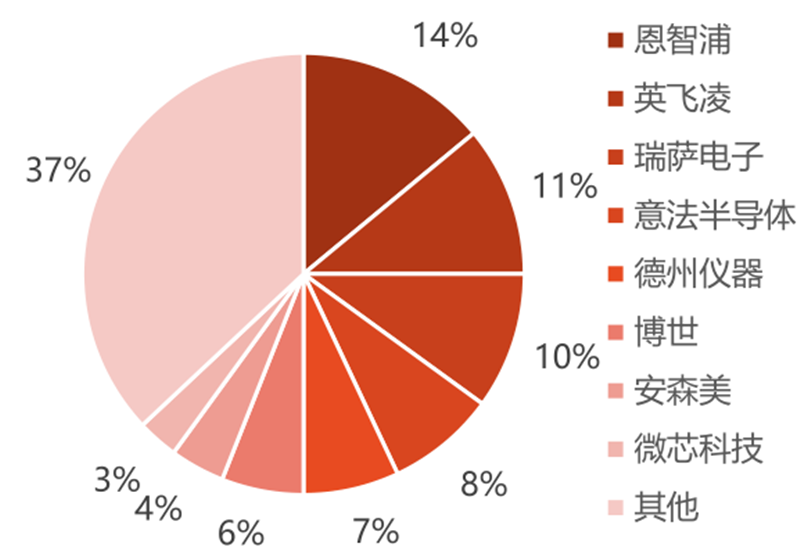
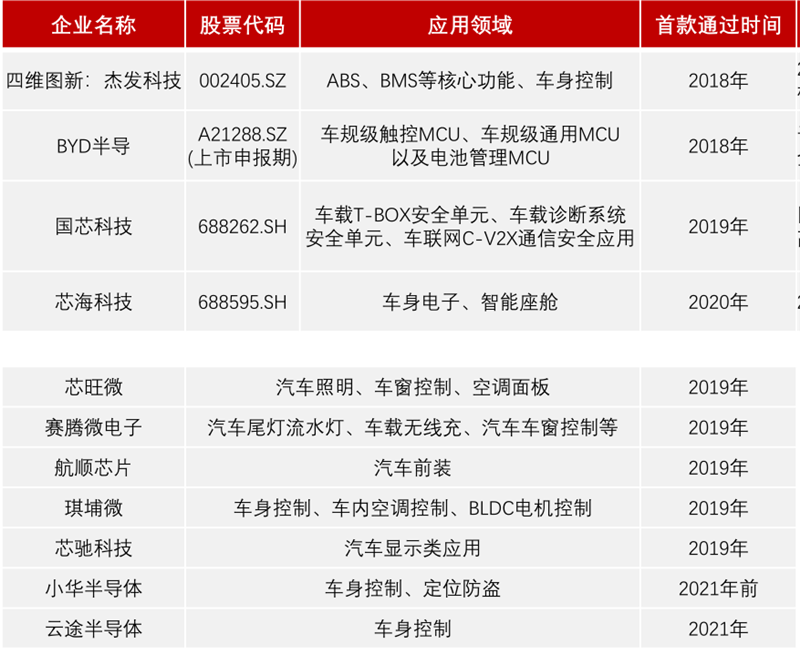
The global market concentration is high, and the trend of domestic substitution continues